# Z-Way Binding

Z-Way is a software to configure and control a Z-Wave network. The software comes with a full stack from Z-Wave transceiver with certified firmware to a REST API on high level.
Z-Way (opens new window) comes in three parts:
- a firmware that runs on the Z-Wave transceiver chip
- the communication stack that runs on different host Operating Systems
- an automation engine and optionally a web server to implement a User Interface
All parts together represents a smart home controller for Z-Wave.
The entire infrastructure is maintained and developed by Z-Wave.Me (opens new window) with the help of a large community.
A detailed step-by-step description of the binding configuration is also available on the Z-Wave.Me Support site (opens new window)
Please note the known issues below.
# Approach
The idea behind is the integration of Z-Wave through a bridge (Z-Way controller). The existing, certified Z-Way stack can be used to build, configure and control the Z-Wave network. By using the REST API all devices are loaded from Z-Way and represented as openHAB elements. The sensor data and actuator states are constantly updated and commands are passed to the Z-Way system.
The Binding uses the Z-Way library for Java (GitHub (opens new window)).
# Supported Things
The Z-Way Binding provides different thing types. The core component is the bridge which represents the Z-Way server. For the integration of devices, two thing types are available. In Z-Way there are devices which represent physical devices and (virtual) devices which are defined in Apps. The difference is that physical devices usually have several functions. Z-Way server constructs (virtual) devices for each function, such as motion sensors or door contacts. In openHAB, these functions are bundled into physical devices and represented as things with channels for each function. This type of thing is a Z-Wave Device. On the other hand all virtual devices are mapped to Z-Way Virtual Devices with exactly one channel.
- Z-Way Server (Bridge) represents a bridge with general settings and communication tasks.
- Z-Way Virtual Device represents one (virtual) device with the corresponding channel. A bridge is necessary as an intermediary between openHAB thing and Z-Way device.
- Z-Wave Device represents a device of real world. Each device function will be mapped to a separate channel. The bridge is necessary as an intermediary between openHAB thing and Z-Way device.
# Discovery
A discovery service for Z-Way servers scans local network and must always be started manually. Z-Way doesn't support any discovery protocol like UPnP for this purpose. That is why first all IP addresses in local network are checked on port 8083. If the server answers, a ZAutomation request (/ZAutomation/api/v1/status) is performed to ensure, the found server runs Z-Way.
Another discovery service provides available devices (a configured bridge is necessary). The device discovery service is performed at a specified interval, but can also be started manually.
Note: In the Z-Way server device can be disabled or made invisible. Only for active and visible Z-Way devices channels will created.
# Binding Configuration
No configuration is necessary.
# Thing Configuration
The textual configuration (via *.thing files) isn't useful because the resulting elements are read-only. But the configuration and properties of things are changed at runtime and channels are dynamically added and removed.
# Z-Way Server (Bridge)
Besides the username and password all required Z-Way information are found during discovery.
| Configuration Name | Mandatory | Default | Desciption |
|---|---|---|---|
| zwayServerIpAddress | localhost | The IP address or hostname of the Z-Way server. If Z-Way and openHAB are running on the same machine, the default value can be used. | |
| zwayServerPort | 8083 | The port of the Z-Way server (1 to 65535) | |
| zwayServerProtocol | http | Protocol to connect to the Z-Way server (http or https) | |
| zwayServerUsername | admin | Username to access the Z-Way server. | |
| zwayServerPassword | X | Password to access the Z-Way server. | |
| pollingInterval | 3600 | Refresh device states and registration from Z-Way server in seconds (at least 60). |
Only the Z-Way server can be configured textual:
Bridge zway:zwayServer:192_168_2_42 [ zwayServerIpAddress="localhost", zwayServerPort=8083, zwayServerProtocol="http", zwayServerUsername="admin", zwayServerPassword="admin", pollingInterval=3600 ] {
// associated things have to be created with the UI
}
# Z-Way Virtual Device
| Configuration Name | Mandatory | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| deviceId | X | Device ID of virtual device | |
| bridge reference | X |
# Z-Wave Device
| Configuration Name | Mandatory | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| nodeId | X | Node ID of the Z-Wave device | |
| bridge reference | X |
# Channels
# Channels with detailed information for the devices
The following channels are currently supported.
| Channel Type ID | Item Type | Category | Asssigned for Z-Way device type and probe type |
|---|---|---|---|
| sensorTemperature | Number | Temperature | SensorMultilevel - temperature |
| sensorLuminosity | Number | Light | SensorMultilevel - luminosity |
| sensorHumidity | Number | Humidity | SensorMultilevel - humidity |
| sensorBarometer | Number | Pressure | SensorMultilevel - barometer |
| sensorUltraviolet | Number | Light | SensorMultilevel - ultraviolet |
| sensorCO2 | Number | CarbonDioxide | SensorMultilevel - Special case: no probe type for carbon dioxide sensors available - probe title CO2 Level acts as selection criterion |
| sensorEnergy | Number | Energy | SensorMultilevel - energy |
| sensorMeterKWh | Number | Energy | SensorMultilevel - meterElectric_kilowatt_per_hour |
| sensorMeterW | Number | Energy | SensorMultilevel - meterElectric_watt |
| sensorSmoke | Switch | Smoke | SensorBinary - smoke |
| sensorCo | Switch | Gas | SensorBinary - co |
| sensorFlood | Switch | Water | SensorBinary - flood |
| sensorTamper | Switch | Alarm | SensorBinary - tamper |
| sensorDoorWindow | Contact | Contact | SensorBinary - door-window |
| sensorMotion | Switch | Motion | SensorBinary - general_purpose, motion |
| switchPowerOutlet | Switch | PowerOutlet | SwitchBinary - Special case: no probe type for power outlet available - icon switch acts as selection criterion |
| switchColorTemperature | Dimmer | ColorLight | SwitchMultilevel - switchColor_soft_white, switchColor_cold_white |
| thermostatMode | Switch | Temperature | SwitchBinary - thermostat_mode |
Currently unsupported Z-Way probe types:
- SensorBinary: cooling, all alarm types (resulting from Z-Wave command class AlarmSensor(deprecated) and Alarm)
- SensorMultilevel: meterElectric_pulse_count, meterElectric_voltage, meterElectric_ampere, meterElectric_power_factor
# Universial channels for the devices
The following channels represent universial channels if no further device information are available, only depending on the Z-Way device types (for available device types see Z-Way Documentation (opens new window)).
| Channel Type ID | Item Type | Category | Assigned for Z-Way device type |
|---|---|---|---|
| battery | Number | Battery | Battery |
| doorlock | Switch | Door | Doorlock |
| sensorBinary | Switch | Switch | SensorBinary |
| sensorMultilevel | Number | - | SensorMultilevel |
| switchBinary | Switch | Switch | SwitchBinary |
| switchMultilevel | Dimmer | - | SwitchMultilevel |
| switchColor | Color | ColorLight | SwitchRGBW |
| switchControl | Switch | Switch | SwitchControl, ToggleButton, SwitchToggle |
| thermostat | Number | Temperature | Thermostat |
| sensorDiscrete | Number | - | SensorDiscrete |
Unsupported Z-Way device types: Camera, SensorMultiline, Text. The integration of these types isn't planned.
# Channels for the Z-Way Server (Bridge)
| Channel Type ID | Item Type | Category | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| actions | String | - | It is currently possible to update all devices. |
| secureInclusion | Switch | Switch | Change inclusion type for further inclusions. |
| inclusion | Switch | Switch | Start inclusion mode (after a timeout the inclusion will be automatically finished). |
| exclusion | Switch | Switch | Start exclusion mode (after a timeout the exclusion will be automatically finished). |
# Locations
The locations of the Z-Way devices are loaded during the discovery. Based on the location ID of Z-Way device, the name of the Z-Way room is then allocated to the location property of the thing.
# Developer stuff
# Known issues
- The Z-Way Binding only works, when simple mode of item linking is enabled during thing creation.
# Structure of Z-Way Binding
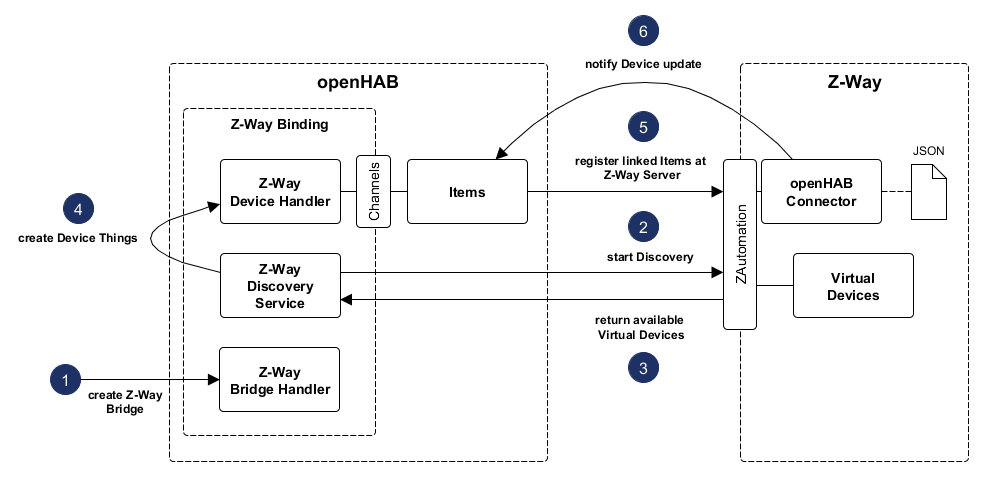
# Features
- Discovery of the Z-Way server and devices
- Control of the Z-Wave devices in openHAB
- Receive updates of sensor data and actuator states in openHAB
# Restrictions
- Z-Way device types (especially the probe types) supported by openHAB channels with detailed information (scale types and so on) are not complete.
- Configuration of the Z-Wave network by the binding is currently not possible (physical device configuration)
- Only polling is available. Further versions will contain other mechanisms under usage of the WebSocket implementation of Z-Way or MQTT.
